Project description:
The objective of this project is the development of high performance functional materials by in situ generation of micro and nanostructured phases through the application of a strategic methodology based on computational thermodynamics.
The nanostructured materials proposed here will be obtained through an in situ formation approach, that is, in which the final material is formed through reactions between the selected raw materials during sintering, which, seeking to reach thermodynamic equilibrium, undergo a nano/microstructural evolution of interest.
In this research, design and optimization techniques will be developed for intelligent acoustic metamaterials (MMA) with a sub-wavelength scale, for the control of sound absorption and insulation in automotive vehicles, aircraft, machinery, mechanical systems that generate noise and vibration. This stage of the project will be carried out in partnership between the LVA and the Materials Laboratory (LabMat) at UFSC.
The nanostructured metallic materials to be developed in this project have a disruptive potential for the metalworking industry, because when technology transfer to industry is in view, high productivity techniques are needed that enable savings in raw materials and energy. In situ powder metallurgy techniques, associated with computational thermodynamics, provide a change in the production paradigm, which is often associated with high cost and complexity and difficult reproducibility.
Coordinator/Participants:
Prof. Aloisio Nelmo Klein (coordinator, LabMat); Prof. Erasmo Felipe Vergara (collaborator); Prof. Archangel Lenzi (collaborator); Gildean do Nascimento Almeida (collaborator).
Partners: Materials Laboratory (LabMat/UFSC); Financier of Studies and Projects (Finep); Education and Engineering Foundation of Santa Catarina (FEESC).
Project Description: Despite the numerous advantages caused by the innovation and automation of exams, it is observed that in Brazil there are few software aimed at the evaluation of hearing loss, and this is due to numerous questions, among them: the lack of technology that the country faces and the high cost involved in importing technologies from other countries. Another relevant problem is the scarcity of training and assistance needed to ensure the proper use of these technologies. To address the lack of software with technology at national and seeking to promote standardized tests aimed at the evaluation of hearing loss and that bring reliable results, a free platform for audiology evaluation is being developed, called perSONA.
Coordinator/ Participants: Prof. Stephan Paul (coordinator); Profa. Maria Madalena Canina Pinheiro (participant / Fonoaudiologia UFSC); Profa. Fernanda Zucki (participant / Fonoaudiologia UFSC) Bruna de Oliveira Bagnara (student / Fonoaudiologia UFSC); Gustavo Trentin (participant); Bernardo Murta (alumni); Ângelo Lara (participant).
Partners: Course of Phonoaudiology UFSC.
To learn more about this project, visit the page: http://persona.ufsc.br/
Project images:
 Image 1: Software perSONA – Module Tonal Audiometry – Teaching. |
 Image 2: Software perSONA – Module Evaluation of Speech Perception in Noise. |
 Image 3: Software perSONA – Test application. |
 Image 4: Software perSONA – Audiometry History. |
 Image 5: Software perSONA – Main screen. |
|
Project Description: The social remoteness caused by COVID-19 has caused changes in the dynamics of cities around the world. The measures to restrict the use of public and collective spaces caused, by reducing circulation, work and leisure, reduction of sound pressure levels (níveis de pressão sonora – NPS) of environmental noise. In view of the social isolation, the needs of people in the cities for new challenges in the field of buildings, the urban and sound environment were observed. In order to investigate the sound perception of the inhabited space, an online questionnaire entitled “Survey of the sound perception of the inhabited space before the COVID-19 pandemic”, which began on May 7, 2020. The link to access the form is https://forms.gle/ABxiW193pHWoRQUeA. This research seeks to understand the perception of individuals in relation to their habitable environment and the outdoor spaces of their locality (neighbourhood, city), to discuss possible post-pandemic changes. It is expected that from the questionnaire it is possible to analyze and compare different contexts in Brazil. It is estimated to reach a sample of 1,500 volunteer participants. The results will be reproduced through graphs, tables and maps, being published in indexed scientific journals, and observing aspects relevant to a reflection on the theme of acoustic comfort of the population in coping with future habitability behaviors in the face of viral scenarios. Therefore, the research will bring benefits to the collectivity, since it seeks to contribute to greater knowledge of the spatial needs of the population, with an emphasis on noise pollution and the acoustic comfort of its inhabitants.
Coordinator/Participants: Prof. Erasmo Felipe Vergara (coordinator); Profa. Lizandra Garcia Lupi Vergara (collaborator/ UFSC); Profa. Maria Lúcia Gondim da Rosa Oiticica (collaborator/ UFAL); Gildean do Nascimento Almeida (participant/ LVA UFSC); Lincoln César Bastos Farias (participant/ LVA UFSC); Poliana Lopes de Oliveira (collaborator/ UFSC); Bruna Soares Alencar (collaborator/ UFSC); Ricardo Netto Carminatti (collaborator/ UFSC).
Project images:
Project Description: Topological optimization in continuous media is defined as a material distribution problem within a fixed design domain, in order to obtain a structure that best functions a given function. This methodology, however, presents numerical instabilities intrinsic to its formulation when its is applied to vibratory and harmonic problems. The main objective of this work is to generate continuous structures that present low vibration levels for certain frequency ranges.
Coordinator/ Participants: Dr. Olavo M. Silva (coordinator); Prof. Arcanjo Lenzi (collaborator); Prof. Eduardo Lenz Cardoso (UDESC, collaborator); Prof. Miguel Matos Neves (IST, collaborator).
Partners: Mechanical Engineering UDESC/ Joinville; Superior Technical Institute/ Lisbon
Project images:
 Image 1: Structure (EPT) set, subjected to harmonic excitation. Red: steel. Blue: empty. |
 Image 2: Vibration of an optimized structure. |
Project Description: The noise and vibration control techniques used to increase the absorption capacity of materials and attenuation in divisive elements are of utmost importance in several applications: aeronautical cabins, vehicle compartments, machine enclosures, road traffic barriers, hearing protectors, concert halls and auditoriums in general. However, these techniques have limitations in low frequency ranges, which has motivated research and development of new concepts and acoustic devices. Thus, acoustic metamaterials (metamateriais acústicos MMA) have been shown to be innovative solutions for noise control, with great potential to act efficiently in the absorption and reduction of noise at frequencies below 1,000 Hz. MMA’s are known as periodic structures that have specific physical properties and behavior for large wavelengths (low frequencies). In this research project, the characterization, evaluation and analysis of MMA proposals of labyrinthic types, microperforated panel and Helmholtz resonator, will be developed to study the behavior of both the absorption coefficient and the loss of sound transmission in the frequency region between 100 and 600 Hz, aiming to optimize the acoustic performance of MMA models, in terms of their geometric parameters, visco-thermal effects and acoustic impedance. This investigation will be carried out over 36 months and in five steps: Analytical description of MMA models; Representation of physical and geometrical models of MMA; Modeling and simulation by finite element method; Influence analysis and model optimization; Tests of absorption bench and sound transmission.
Coordinator/Participants: Erasmo Felipe Vergara (coordinator); Prof. Robert Birch (collaborator/ University of Liverpool); Prof. Paulo Mareze (participant Engenharia Acústica/ UFSM); Leandro Rodrigues Barbosa (participant/ Wave consultoria); Prof. Arcanjo Lenzi (collaborator/ LVA UFSC).
Project images:
Project Description: This research project aims to develop a methodology for the design of acoustic metamaterials based on the optimization of the distribution of rigid micro-ducts in a given pre-established space. The priority is to maximize the sound absorption of these metamaterials for “low frequencies” (remembering that the concept of “low frequency” depends on the dimensions involved and the specific application). Additive manufacturing methodologies are investigated for the production and testing of the configurations obtained.
Coordinator/ Participants: Dr. Olavo M. Silva (coordinator); Prof. Arcanjo Lenzi (collaborator).
Partners: Aerospace Engineering/ UFSC; National Industrial Learning Service (Serviço Nacional de Aprendizagem Industrial – SENAI)/ Joinville.
Project images:
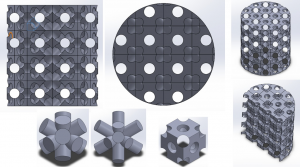 Image 1: Constructive aspects of metamaterial. |
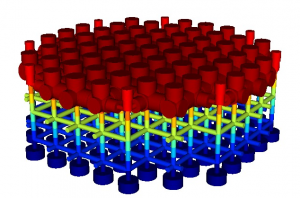 Image 2: Duct networks for different frequency ranges of interest. |
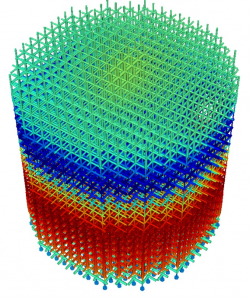 Image 3: Duct networks for different frequency ranges of interest. |
|
Project Description: It is known that noise pollution in hospitals affects the health of both patients and the technical team of health care (doctors, nursers, technicians). Most of the hospital environment is affected by the noise of equipment and machines with high sound pressure levels (níveis de pressão sonora – NPS). The main objective of this joint project is to carry out an assessment of noise pollution in hospital environments (emergency room, operating room and emergency) in Brazil and the USA to investigate the effects on the patient health care care community. It is planned to carry out a survey of the sound pressure levels of noise sources (equipment and machinery) to control and reduce noise in hospital locations through the use of technical and engineering principles applied to rehabilitate the hospital environment. This project will have a significant impact by identifying the sound pressure levels of noise exposure, stress factors in a noisy environment and to reduce discomfort and anxiety caused by noise in workers. This research will be developed in partnership by the proponent and coordinator of the guidance team of the Laboratory of Vibrations and Acoustic (LVA), Comfort Laboratory (Laboratório de Conforto – Labcon) of UFSC and the research team of Professor Olivia C. Coiado of the Carle Illinois School of Medicine, University of Illinois (USA) and aims to increase interdisciplinarity in medical and engineering education by integrating noise exposure in hospital workplaces.
Coordinator/Participants: Prof. Erasmo Felipe Vergara (coordinator); Profa. Olivia C. Coiado (collaborator/ University of Illinois); Profa. Lizandra Garcia Lupi Vergara (collaborator/ UFSC); Gildean do Nascimento Almeida (participant/ LVA UFSC); Linconl César Bastos Farias (participant/ LVA UFSC); André Luis Zanella (participant/ UFSC); Poliana Lopes de Oliveira (collaborator/ UFSC); Bruna Soares Alencar (collaborator/ UFSC)
Project Description: The project aims to study the effects of installation of propellers and the interaction between multiple rotors in noise generated by distributed electric propulsion aircraft. The studies are divided into two fronts: experimental and numerical. The experimental part consists of the construction of a test bench for semi-anechoic chamber tests. The numerical front of this project focuses on the development of models in Lattice-Boltzmann, through the commercial software PowerFLOW.
Coordinator/ Participants: Prof Júlio Apolinário Cordioli (coordinator); M. Eng. Lucas Araújo Bonomo (participant LVA/UFSC); Isabela Canello Resener (participant/ LVA UFSC); Prof. Andrey Ricardo da Silva (collaborator/ LVA UFSC).
Partners: EMBRAER.
Project images:
 Image 1: Prototype aircraft with distributed propulsion. |
 Image 2: eVTOL aircraft concept. |
Project Description: This project aims to carry out the processing of seismic data already acquired in the section referring to the water column, integrating oceanography and seismic reflection, to obtain oceanographic parameters. Objective processing details the behavior of sound speed and temperature in the water column, as well as remotely identifying water bodies and the presence of internal waves, as a subsidy for increasing the quality of subsurface imaging during seismic surveys. The estimation of these parameters by acoustic methods brings two major advantages over conventional measurement methods: (1) the possibility of estimating the parameters using the reflection seismic data themselves, which makes it unnecessary to stop vessels during withdrawals for CTD or XBT measurements and (2) much larger sampling of the environment, allowing the use of much more detailed models in the correction of overtime and migration of seismic measurement data. The creation of new, more detailed models of sound speed in the water column, brings a significant improvement in seismic data processing, increasing the quality of the seismograms obtained and, consequently, facilitating the location and monitoring of oil and gas wells and other subsurfaces structures.
Coordinator/ Participants: Prof. Antônio Henrique da F. Klein (coordinator); Prof. Stephan Paul (collaborator); Prof. Antônio Fernando Härter Fetter Filho (collaborator); Josafat Ribeiro Filho (participant);
Partners: Course of Oceanography UFSC.
To learn more about this project, visit the page: https://velsom.ufsc.br/equipe/
Project image:
 Flowchart organized by Josafat Ribeiro. |
Project Description: For various industry sectors today, predictive maintenance has become recognized as the best maintenance strategy. Industries with high-cost machines or that need to run for long periods without downs, are examples of sectors where predictive maintenance is essential. Thus, the health of a machine is commonly monitored with vibration sensors to predict possible failures and define where they can occur. These sensors should have great autonomy, be compact and preferably wireless. Because in this way, the operator can perform readings remotely, install them easily in places with limited space and keep the sensor in place for long periods of time without having to spend resources on multiple installations. Electrical devices like these have experienced a great technological advance that has caused a rapid reduction in their electrical consumption. This reduction allowed various forms of energy capture from the environment to replace or complement traditional batteries. These energy capture devices or Energy Harvester (EH) can make use of various forms of energy that are available in the environment, such as solar, thermal, chemical and mechanical energy. The latter has the advantage of being sustainable, stable and small, besides being able to capture energy from various sources such as industry machinery and equipment, vehicles, human movement and fluids. This project aims to investigate EHs alternatives for capturing energy from vibrations as a way to increase the life of sensors for monitoring vibrations used in predictive maintenance processes.
Coordinator/ Participants: Prof. Júlio Apolinário Cordioli (coordinator); Guilherme Cartagena Mirón (participant/ LVA UFSC); Airton José Schmidt Júnior (participant LVA/UFSC); Gabriel Rogério da Silva (participant/ LVA UFSC); Danilo Braga (participant/ Dynamox)
Partners: Dynamox.
Project images:
 Image 1: Finite element simulations of Energy Harvester MEMS devices. |
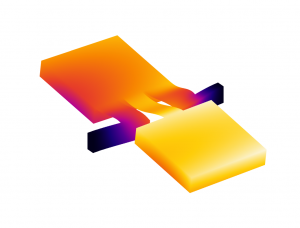 Image 2: Finite element simulations of Energy Harvester MEMS devices. |
 Image 3: Dynamox’s analysis and prognostic technology is part of industry 4.0’s fourth industrial revolution. |
 Image 4: Examples of DynaLogger positioning and illustration of DynaPredict’s fault prediction tools. |
 Image 5: Reading temperature and vibration data by the DynaPredict application of sensors installed in the bearing of a crusher. |
|































